| Version 27 (modified by , 9 years ago) ( diff ) |
|---|
IPv6 in a Campus Network Hands - On
In this Hands-on you will be given a virtual campus LAN. You will configure devices (Cisco based) in both IPv4 and IPv6. After the configurations, you will get a virtual campus network with IPv4/IPv6 dual stack. Each institute you represent will be given a campus LAN. Those who represent the same institutes have to work together as a group, everybody in the group will get a single campus network (remember to sit together in a same row)
Your virtual campus network will then be connected to the virtual PCs (VMs) exactly as real PCs and also to to the real Internet that let you to see how real data passes through your virtual campus network. You will be browsing Internet, checking email, etc through this virtual campus network. This emulation of the campus network has been done by the use of Dynagen/Dynamips.
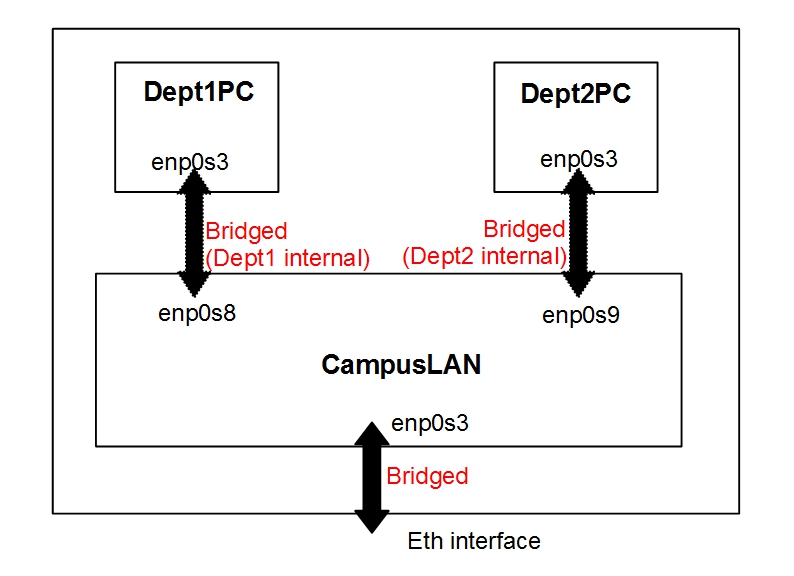
The whole setup reside in three VMs.
- VM for the Campus LAN (Dynage/Dynamips installed)
- Two VMs for the Department PCs
All three VMs (Ubuntu 64) have already been created as Virtul Hard Disk (in VDI format) and available for you to quickly download. They can be easily launched using Oracle Virtual Box. You will also get the complete topology file in the CampusLAN VM. The other two VMs will be used as PCs, or servers located at user end of your campus LAN.
Setting up the Virtualbox
Installation of virtualbox and Downloading virtual hard disks
- Download and install virtualbox 5.0.x
- Download the Virtual Hard disks from the LEARN mirror. You can get them by following links
- Note down the location of downloaded vdi files
Creating the VM CampusLAN
- Start VirtualBox and Click on New button (at top-right) to create new virtual machine
- Enter name of the VM as CampusLAN
- Select OS Type: Linux
- Select Version: Ubuntu (64-bit)
- Then click on Continue button
- Set VM's memory size to 1536MB and click on Continue button
- Set VM's hard disk option to Use an existing virtual hard disk file and click the browse button and browse to the location where you download the virtual hard disks. Then select the CampusLAN.vdi file and click on the create button.
- You will see a new virtual machine named CampusLAN appears on Virtual Box Manager Window
Setting up Network Interfaces
- Select the CampusLAN VM from left panel on Virtual box, right click and open Settings
- Click on the Network title
- On Adapter 1 check the Enable Network Adapter . Then change Attached to be to the Bridged Adapter and make sure the name of the interface is the same interface which you use to connect to the outside (Either Wi-Fi or Ethernet). This virtual interface will work as the WAN port of the of your virtual campus network that can be used to connect from out side.
- Click on Advanced drop down list and change the promiscuous mode to Allow All
- On Adapter 2 check the Enable Network Adapter . Then change Attached to be to the Internal Network and give the Name of the network as Dept1. This virtual interface will connect to a internal virtual bridged network.
- Click on Advanced drop down list and change the promiscuous mode to Allow All
- On Adapter 3 check the Enable Network Adapter . Then change Attached to be to the Internal Network and give the Name of the network as Dept2. This virtual interface will connect to a internal virtual bridged network.
- Click on Advanced drop down list and change the promiscuous mode to Allow All
- Click OK
Adding processors
- Select the CampusLAN VM from left panel on Virtual box, right click and open Settings
- Click on the System title
- Go to Processor tab and set processors to 2
- Click ok
Creating the VM Dept1PC
- Start virtualbox and Click on New button (at top-right) to create new virtual machine
- Enter name of the VM as Dept1PC
- Select OS Type: Linux
- Select Version: Ubuntu (64-bit)
- Then click on Continue button
- Set VM's memory size to 512MB and click on Continue button
- Set VM's hard disk option to Use an existing virtual hard disk file and click the browse button and browse to the location where you download the virtual hard disks. Then select the Dept1PC.vdi file and click on the create button.
- You will see a new virtual machine named Dept1PC appears on Virtual Box Manager Window
Setting up Network Interface
- Select the Dept1PC VM from left panel on Virtual box, right click and open Settings
- Click on the Network title
- On Adapter 1 check the Enable Network Adapter . Then change Attached to be to the Internal Network and give the Name of the network as Dept1. This virtual interface will connect to a internal virtual bridged network.
- Click on Advaned drop down list and change the promiscuous mode to Allow All
- Click OK
Creating the VM Dept2PC
- Start virtualbox and Click on New button (at top-right) to create new virtual machine
- Enter name of the VM as Dept2PC
- Select OS Type: Linux
- Select Version: Ubuntu (64-bit)
- Then click on Continue button
- Set VM's memory size to 512MB and click on Continue button
- Set VM's hard disk option to Use an existing virtual hard disk file and click the browse button and browse to the location where you download the virtual hard disks. Then select the Dept2PC.vdi file and click on the create button.
- You will see a new virtual machine named Dept2PC appears on Virtual Box Manager Window
Setting up Network Interface
- Select the Dept1PC VM from left panel on Virtual box, right click and open Settings
- Click on the Network title
- On Adapter 1 check the Enable Network Adapter . Then change Attached to be to the Internal Network and give the Name of the network as Dept2. This virtual interface will connect to a internal virtual bridged network.
- Click on Advaned drop down list and change the promiscuous mode to Allow All
- Click OK
After Creating all three VM's. Your VM setup will look like this.
Setting UP IP Addresses
CampusLAN VM
Before running Dynagen you have to start your VMs and assign IP address to the VM's network interfaces.
- Select the CampusLAN VM from left panel on Virtual box, right click Start and wait till the VM starts
- login to the machine using the following user credentials
usrname : learn password : <classpassword>
- Then change the interfaces file. Root password is the same as class password
sudo vi /etc/network/interfaces
- locate the following lines
iface enp0s3 inet static address 192.168.56.2 netmask 255.255.255.0 network 192.168.56.0 broadcast 192.168.56.255 gateway 192.168.56.1 dns-nameservers 192.248.1.161
- Change it to the following lines. You can find your IP Address from this table
iface enp0s3 inet static address <Your IP Address > netmask 255.255.255.0 network 192.248.6.0 broadcast 192.248.6.255 gateway 192.248.6.254 dns-nameservers 192.248.1.161
- Save and Exit the editor (type :wq)
- When you completed the IP settings , reboot the machine
sudo reboot
- Confirm the correct IP settings by ipconfig command. Your result should be something like the following. Check the IP address of enp0s3 Interface and see whether the other interfaces are up
enp0s3 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:8c:e0:26 inet addr:<your IP address> Bcast:192.248.6.255 Mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:fe8c:e026/64 Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:1120 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:7550 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:99387 (99.3 KB) TX bytes:567441 (567.4 KB) enp0s8 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:f0:f7:66 inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:fef0:f766/64 Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:8 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:648 (648.0 B) enp0s9 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:51:68:d3 inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:fe51:68d3/64 Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:8 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:648 (648.0 B) lo Link encap:Local Loopback inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0 inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1 RX packets:160 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:160 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1 RX bytes:11840 (11.8 KB) TX bytes:11840 (11.8 KB) - Try ping to some known hosts and see the results.
ping 192.248.6.254 ping 192.248.1.161 ping www.google.com
Dept1PC VM
As this is a PC inside your virtual LAN it has a private IP address. The address is already configured. You can verify whether it is correct.
- Select the Dept1PC VM from left panel on Virtual box, right click Start and wait till the VM starts
- login to the machine using the following user credentials
usrname : learn password : <classpassword>
- Check the IP address by using the command ifconfig. The result should be as following.
enp0s3 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:e9:76:20 inet addr:10.0.10.1 Bcast:10.0.10.255 Mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:fee9:7620/64 Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:198 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:71 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:23291 (23.2 KB) TX bytes:15516 (15.5 KB) lo Link encap:Local Loopback inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0 inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1 RX packets:160 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:160 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1 RX bytes:11840 (11.8 KB) TX bytes:11840 (11.8 KB)
Dept2PC VM
As this is a PC inside your virtual LAN it has a private IP address. The address is already configured. You can verify whether it is correct.
- Select the Dept2PC VM from left panel on Virtual box, right click Start and wait till the VM starts
- login to the machine using the following user credentials
usrname : learn password : <classpassword>
- Check the IP address by using the command ifconfig. The result should be as following.
enp0s3 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:e6:60:87 inet addr:10.0.20.1 Bcast:10.0.20.255 Mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:fee6:6087/64 Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:286 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:830 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:35607 (35.6 KB) TX bytes:61166 (61.1 KB) lo Link encap:Local Loopback inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0 inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1 RX packets:686 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:686 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1 RX bytes:58320 (58.3 KB) TX bytes:58320 (58.3 KB)
Running Dynagen/Dynamips
Dynamips is a Cisco router emulator. It emulates 2691, 3620, 3640, 3660, 3725, 3745, and 7206 hardware platforms, and runs standard IOS images.
Dynagen is a text-based front end for Dynamips, which uses the “Hypervisor” mode for communication with Dynamips. Dynagen simplifies building and working with virtual networks
- First login to CampusLAN VM.
- Change to root user . Enter the command su. And give the password
su password : <class password>
- Then start up the Dynamips server on your local machine
dynamips –H 7100 &
hypervisor will run on port 7100
- You can find the topology file in /var/dynamips/campusLAN.net
- Run the topology file with dynagen
dynagen /var/dynamips/CampusLAN.net
- Now you have the network topology running. Give the following command in dynagen
=> list
- Your result should be something like this
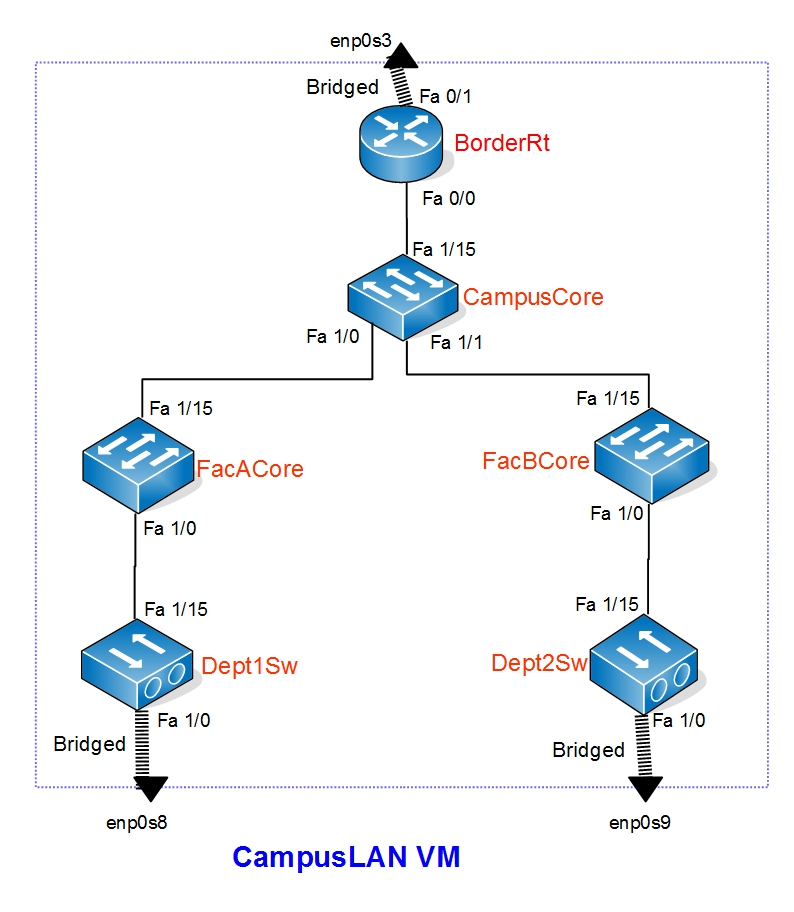
Name Type State Server Console BorderRt 3725 stopped localhost:7100 2100 CampusCore 3725 stopped localhost:7100 2200 FacACore 3725 stopped localhost:7100 2300 FacBCore 3725 stopped localhost:7100 2400 Dept1Sw 3725 stopped localhost:7100 2500 Dept2Sw 3725 stopped localhost:7100 2600
- You can see there are 6 devices. But none of them are running. You can also see the numbers of the ports which the console port of devices are running. This will also be helpful to you in next steps
- you can get details about devices by following command
=> show device <device name>
- This Command will be helpful to know on which interface the devices are connected to each other
=> show device BorderRt Router BorderRt is stopped Hardware is dynamips emulated Cisco 3725 with 256 MB RAM Router's hypervisor runs on localhost:7100, console is on port 2100 Image is shared c3725-adventerprisek9-mz124-15.bin-localhost.ghost with idle-pc value of 0x60a8033c Idle-max value is 100, idlesleep is 30 ms 55 KB NVRAM, 128 MB disk0 size, 0 MB disk1 size slot 0 hardware is GT96100-FE with 2 interfaces FastEthernet0/0 is connected to router CampusCore FastEthernet1/15 FastEthernet0/1 is connected to real enp0s3 interface - Now you can start the devices. To start the devices use the start command
=> start BorderRt => start CampusCore => start FacACore => start FacBCore => start Dept1Sw => start Dept2Sw
- It will take some time to boot up all the devices. After that you will have the following topology up and running and you can start configuring the routers and switches.
Network Topology
Attachments (2)
- InitialTopology.jpg (174.5 KB ) - added by 9 years ago.
- VMSetup.jpg (74.5 KB ) - added by 9 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip